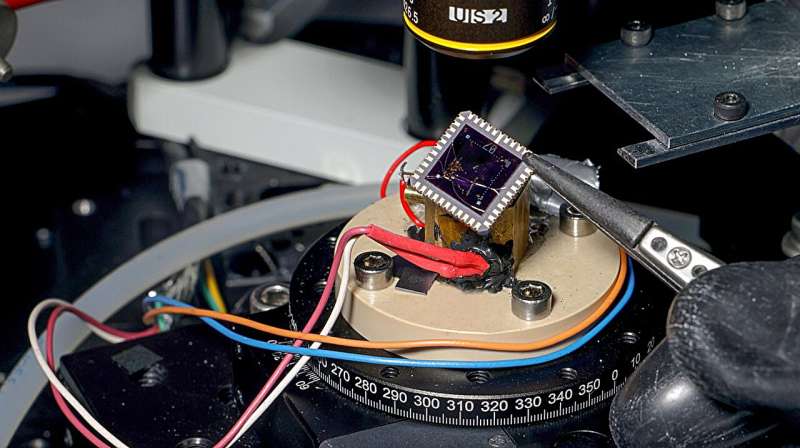
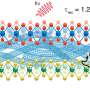
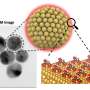
The LANES lab's 2D device made of graphene and indium selenide . Credit: Alain Herzog, Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne
EPFL engineers have created a device that can efficiently convert heat into electrical voltage at temperatures lower than that of outer space. The innovation could help overcome a significant obstacle to the advancement of quantum computing technologies, which require extremely low temperatures to function optimally.
To perform quantum computations, quantum bits (qubits) must be cooled down to temperatures in the millikelvin range (close to -273 Celsius), to slow down atomic motion and minimize noise. However, the electronics used to manage these quantum circuits generate heat, which is difficult to remove at such low temperatures.
Most current technologies must therefore separate quantum circuits from their electronic components, causing noise and inefficiencies that hinder the realization of larger quantum systems beyond the lab.
Researchers in EPFL's Laboratory of Nanoscale Electronics and Structures (LANES), led by Andras Kis, in the School of Engineering have now fabricated a device that not only operates at extremely low temperatures, but does so with efficiency comparable to current technologies at room temperature. The achievement has been published in Nature Nanotechnology.
"We are the first to create a device that matches the conversion efficiency of current technologies, but that operates at the low magnetic fields and ultra-low temperatures required for quantum systems. This work is truly a step ahead," says LANES Ph.D. student Gabriele Pasquale.
The innovative device combines the excellent electrical conductivity of graphene with the semiconductor properties of indium selenide. Only a few atoms thick, it behaves as a two-dimensional object, and this novel combination of materials and structure yields its unprecedented performance.
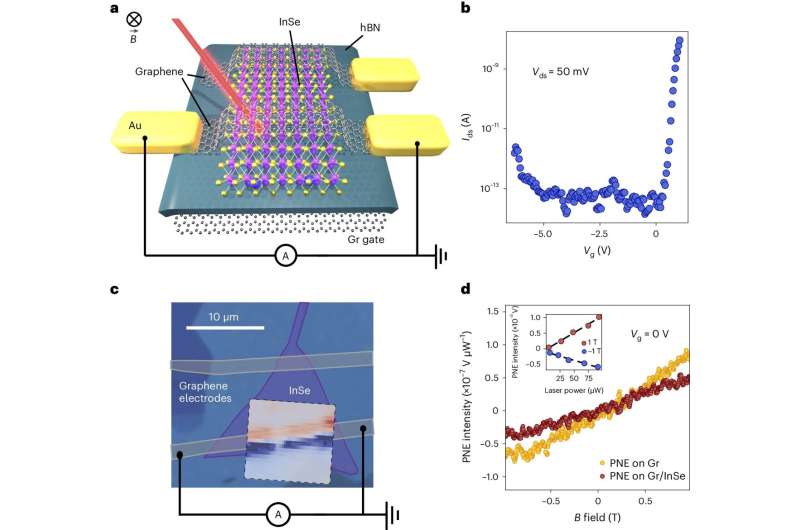
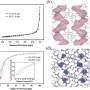
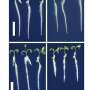
Device schematics and basic characterization. Credit: Nature Nanotechnology (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41565-024-01717-y
Harnessing the Nernst effect
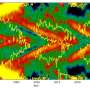
The device exploits the Nernst effect: a complex thermoelectric phenomenon that generates an electrical voltage when a magnetic field is applied perpendicular to an object with a varying temperature. The 2D nature of the lab's device allows the efficiency of this mechanism to be controlled electrically.
The 2D structure was fabricated at the EPFL Center for MicroNanoTechnology and the LANES lab. Experiments involved using a laser as a heat source, and a specialized dilution refrigerator to reach 100 millikelvin—a temperature even colder than outer space.
Converting heat to voltage at such low temperatures is usually extremely challenging, but the novel device and its harnessing of the Nernst effect make this possible, filling a critical gap in quantum technology.
"If you think of a laptop in a cold office, the laptop will still heat up as it operates, causing the temperature of the room to increase as well. In quantum computing systems, there is currently no mechanism to prevent this heat from disturbing the qubits. Our device could provide this necessary cooling," Pasquale says.
A physicist by training, Pasquale emphasizes that this research is significant because it sheds light on thermopower conversion at low temperatures—an underexplored phenomenon until now. Given the high conversion efficiency and the use of potentially manufacturable electronic components, the LANES team also believes their device could already be integrated into existing low-temperature quantum circuits.
"These findings represent a major advancement in nanotechnology and hold promise for developing advanced cooling technologies essential for quantum computing at millikelvin temperatures," Pasquale says. "We believe this achievement could revolutionize cooling systems for future technologies."
More information: Gabriele Pasquale et al, Electrically tunable giant Nernst effect in two-dimensional van der Waals heterostructures, Nature Nanotechnology (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41565-024-01717-y
Journal information: Nature Nanotechnology
Provided by Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne